The Bullwhip Effect
Hasan Nasir
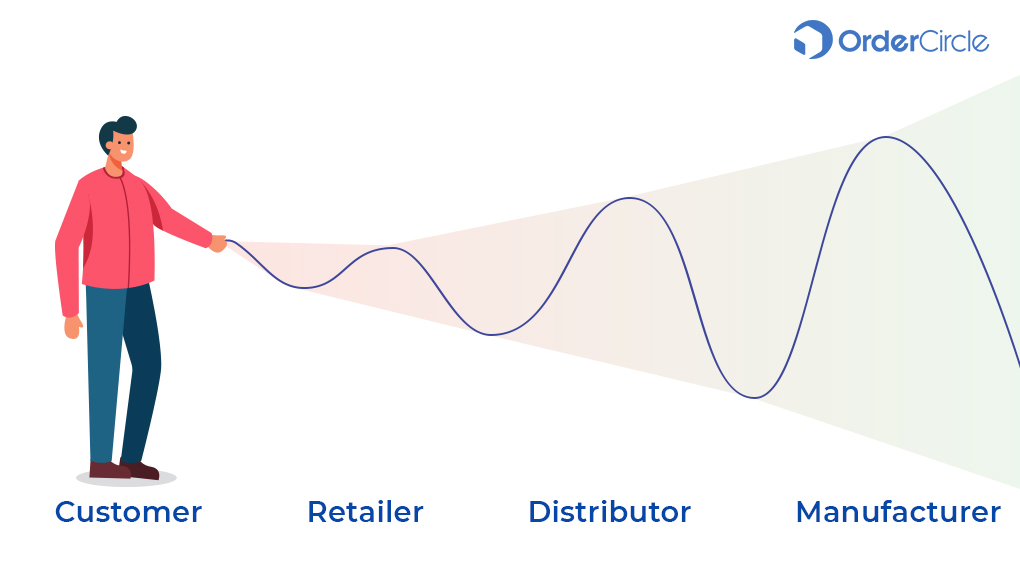
The Bullwhip effect refers to volatility in inventory levels created in response to customer demand. This volatility increases as we move upwards in the supply chain.
This concept was named based on an effect created when a person moves a whip. When someone drives a whip, small movements are created near to the handle. However, as we move further, the movements gradually increase across the whip. Similarly, in a supply chain, customer demand is the handle. A small movement in demand from the customer creates more significant movements in the supply chain. These movements gradually increase as one moves higher up in the chain.
Thus, the Bullwhip effect highlights inefficiencies in a supply chain and distribution system.
Why does this happen?
There are various parties in a supply chain. It starts with a raw material supplier and ends with the customer. Whenever there is an increase in demand from the customer, parties at each stage in the supply chain try to meet it. The assumption is that this surge in demand will continue. Thus, they start stocking more inventory buffer to absorb this additional demand to avoid stock shortages. This stocking results in extra inventory across the supply chain.
Let us understand this with the help of an example:
A retailer keeps 50 units of a chocolate brand in stock. Usually, the retailer sells 10 units a day and replenishes the same amount from the distributor. But one day, the retailer sells 30 units of chocolate. Thus, he assumes customers will start buying more daily. He responds by ordering 50 units from the distributor to meet this increase in demand forecasted. Due to this, the distributor responds by ordering more from the manufacturer. He orders 100 units from the manufacturer to ensure he does not have a shortage. In turn, the manufacturer produces 200 units to build some buffer as he expects a continuation of demand from the distributor. This phenomenon results in an increased inventory level across the supply chain.
What causes the Bullwhip Effect?
Some of the factors contributing to the bullwhip effect are –
- Lack of proper communication – Lack of proper communication in the supply chain can create the Bullwhip effect. This improper communication results in an overestimation of demand and thus excess inventory.
- Order batching– Order batching means placing orders collectively rather than daily. This is done after a certain level of demand is accumulated. Thus, when retailers follow order batching, they do not order uniformly from distributors. Sometimes they may order more, sometimes less. If the distributor misinterprets this, it can result in the bullwhip effect.
- Inaccurate demand forecasting– Demand is usually forecasted based on historical trends. Any inaccuracy in such a forecast could result in the bullwhip effect.
- Price variations – Variation in pricescan distort demand. For example, companies offer products at lower prices in discounted schemes, which increases the demand temporarily. These price variations could lead to inaccurate forecasting and thus over-production.
How to minimize the Bullwhip effect?
One cannot eliminate the bullwhip effect from the supply chain. However, below are some ways in which one can minimize its impact:
- Develop an understanding of this effect – Lack of awareness can result in higher damage from events such as Bullwhip. With proper training and knowledge across the supply chain, organizations can reduce the impact of such events.
- Proper inventory management – Proper management of inventory helps avoid excessive ordering. Organizations cans use inventory management software for the same. They help decide order quantities, forecast seasonal demand, and reduce older products.
- Keep a limited supply chain with proper communication strategy – Oneshould aim to reduce the number of parties in the supply chain. Further, one should ensure better communication in the supply chain. This will help in a better understanding of customer demand and thus reduce the bullwhip effect.
- Collaboration between customers and suppliers – Onecan improve the supply chain efficiency through collaboration between customers and suppliers. This will help in better demand forecasting and lesser inventory.
- Minimize discounted sales: Oneshould aim at reducing the occasional discount offers. Instead, prices should be stabilized throughout the year. This will result in increased sales to regular customers, while one-time customers could be avoided.
Conclusion
Events such as the Bullwhip can result in excessive inventory and reduce profitability. This could prove to be a threat to the business. Such circumstances arise due to a lack of awareness and lack of effective communication. Such events cannot be eliminated from the supply chain. However, proper training and effective communication could help reduce the adverse impact of such events.
